Dangerous Dog Laws
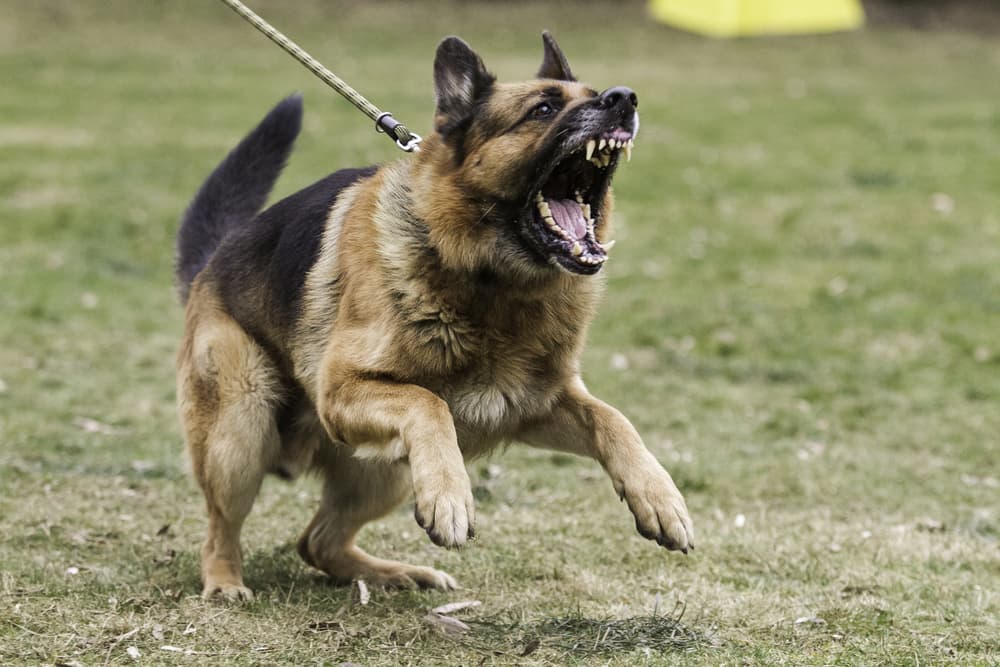

When a dangerous dog attacks or bites a person, serious and sometimes fatal injuries can result. If you suffered injuries in a dog attack incident, various laws may apply, depending on your jurisdiction. In addition to seeking prompt medical treatment after a dog bite incident, you must consult an experienced dog bite lawyer as quickly as possible.
Your lawyer can review your circumstances with you and determine the applicable laws in your case. They may then pursue a claim with the dog owner’s insurance company or file a lawsuit and pursue litigation in the court system on your behalf.
Common Dog Bite Laws
In dog bite laws, the legal landscape centers on the concept of owner liability. When a dog bite occurs, responsibility typically falls on the owner, regardless of whether the canine displayed prior aggression or if the owner was aware of such behavior.
State law may emphasize a one-bite rule principle. This means that dog owners are not automatically liable for the first bite their dog inflicts, but subsequent bites may lead to legal repercussions. However, even for the first bite, liability may still exist if the owner negligently handled or restrained the dog.
Establishing negligence holds dog owners accountable for any damages resulting from a bite. This includes medical expenses that the victim incurred, costs associated with rehabilitation or therapy, and even potential lost income if the victim cannot work due to their injury.
A strict liability standard may apply in some states. If the dog owner is aware that their canine has previously bitten someone or exhibited aggressive behavior, they may be strictly liable for any subsequent bites. In such instances, the owner cannot argue a lack of knowledge about the dog’s aggressive tendencies as a defense.
Furthermore, the law extends beyond bites and covers other forms of aggressive behavior that cause injury. If a dog jumps on someone, causing them to fall and sustain injuries, the owner can still be liable for the resulting harm.
State law also distinguishes between trespassers and non-trespassers regarding dog bite liability. The law generally holds the owner responsible for non-trespassers, assuming negligence or knowledge of the dog’s dangerous propensities. However, in the case of trespassers, the owner may have a reduced duty of care, potentially affecting their liability.
Navigating dog bite laws requires carefully examining the incident’s circumstances. Individuals can effectively navigate the legal landscape and seek appropriate monetary compensation for injuries resulting from a dog bite or aggressive behavior by understanding the one-bite rule, negligence principles, strict liability standards, and the distinction between trespassers and non-trespassers.
Common Injuries Following a Dog Bite or Attack
Dog bite incidents can result in a range of injuries, varying in severity based upon factors such as the dog’s size, breed, and the circumstances of the attack. One of the most common injuries is puncture wounds.
Dogs often have sharp teeth capable of penetrating the skin, leading to deep puncture wounds that may require medical attention. These wounds are painful and pose an increased risk of infection due to the bacteria in a dog’s mouth.
Additionally, lacerations are prevalent in dog bite incidents. Dogs may cause cuts and tears in the skin, leading to visible wounds requiring sutures or other forms of wound closure. The lacerations’ severity depends on the bite’s force and the dog’s size and strength.
Contusions and bruising may accompany dog bite injuries. The force applied during an attack can cause significant bruising, indicating damage to underlying blood vessels and tissues. While discolorations may not be as immediately threatening as puncture wounds or lacerations, they can still result in pain and discomfort for the victim.
Fractures are another serious consequence of dog bites, especially when the attack involves a large or powerful dog. The force of a dog’s bite can lead to broken bones, particularly in the extremities or areas where the dog bites down with substantial force. Fractures may also necessitate surgical intervention and prolonged rehabilitation.
In some cases, nerve damage can occur during a dog bite incident. Dogs may bite sensitive areas, such as the face or hands, causing nerve damage. Nerve injuries can result in pain, numbness, or loss of function in the affected area, requiring specialized medical attention and possibly long-term treatment.
Emotional trauma is a less visible but equally significant consequence of dog bite incidents. Victims may develop post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety, or a fear of dogs after experiencing a traumatic attack. Emotional injuries can have a lasting effect on an individual’s well-being and may require psychological support and therapy.
Understanding the range of injuries that can result from a dog bite incident is crucial for both victims and legal professionals involved in seeking compensation. By recognizing the potential physical and emotional consequences, individuals can pursue appropriate medical treatment and legal remedies to address the effects of a dog bite on their health and overall quality of life.
Important Evidence in Dog Bite Cases
Building a strong case in a dog bite or attack incident requires gathering pertinent evidence to establish liability and quantify damages. One crucial piece of evidence is witness statements.
Eyewitness accounts provide firsthand perspectives on the incident, detailing the dog’s behavior, the owner’s actions, and the extent of the injuries sustained. These statements contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the events leading to the dog bite and can corroborate the victim’s narrative.

Medical records also play a pivotal role in dog bite cases. Documenting the injuries sustained, treatment received, and prognosis outlined by healthcare professionals provides concrete evidence of the physical harm inflicted.
Medical records also help establish a direct link between the dog bite and the resulting injuries, aiding in quantifying damages sought in the legal proceedings.
Photographic evidence is invaluable in portraying the visible aftermath of a dog bite. Taking clear and detailed photos of the injuries shortly after the incident can be powerful documentation. These images provide a visual record of the wounds and help convey the severity and extent of the injuries to legal professionals, insurance adjusters, and, if necessary, a court.
Animal control reports are often essential evidence in dog bite cases. These reports document the aggressive tendencies or history of the dog involved, shedding light on whether the owner was aware of the animal’s potential danger. This evidence can be critical in establishing negligence and, in certain cases, imposing strict liability on the dog owner.
Additionally, any history of previous incidents involving the same dog is crucial evidence. Records of prior bites or aggressive behavior contribute to assessing the dog’s propensity for violence. This information is instrumental in determining whether the dog owner should have taken precautions to prevent the incident.
Cases alleging negligence, leash laws, and relevant ordinances are crucial evidence. Violations of these regulations, such as allowing a dog to roam unrestrained in public spaces, can strengthen the argument that the owner failed to exercise reasonable care in preventing the dog bite.
Individuals pursuing a dog bite case can construct a compelling narrative by meticulously gathering and presenting these pieces of evidence.
This comprehensive approach, combining eyewitness accounts, medical records, photographs, animal control reports, and any relevant legal regulations, enhances the likelihood of a successful resolution, ensuring that victims receive fair compensation for the physical and emotional consequences of a dog bite or attack.
Settling or Litigating a Dog Bite Case
Resolving a dog bite case in the legal realm involves a strategic decision between settling or litigating, with various factors influencing the chosen course of action.
Settlement negotiations often emerge as an initial step. In these discussions, the victim’s legal representative engages with the dog owner’s insurer or legal representatives to reach a compensation agreement. Settlements can provide a quicker resolution, sparing both parties the time and costs of prolonged litigation.
Settlements hinge on a negotiation process wherein the victim’s attorney presents a compelling case backed by evidence such as medical records, photographs, witness statements, and any relevant ordinances or regulations.
Your dog bite lawyer will establish liability, quantify damages, and secure a fair and comprehensive compensation package for the victim. The negotiation process allows flexibility and can lead to a mutually agreeable resolution without needing a protracted legal battle.
However, settlement may not always be feasible or desirable. In cases where the dog owner disputes liability or the offered settlement is insufficient to cover the victim’s losses, litigation may become the preferred course of action.
Filing a lawsuit involves:
- Initiating legal proceedings.
- Presenting the case in court.
- Allowing a judge or jury to determine the outcome.
Litigation requires a more extensive and formalized presentation of evidence, with both parties presenting their arguments and witnesses in a structured legal setting.
The court process involves adherence to legal procedures, including discovery, where each side collects evidence from the other, and court appearances to present arguments and evidence. The litigation path is typically more time-consuming and can escalate legal costs.
Ultimately, deciding to settle or litigate a dog bite case depends on various factors, including the strength of the evidence, the willingness of the parties to negotiate, and the desire for a timely resolution.
Attorneys play a crucial role in advising clients on the advantages and drawbacks of each option, guiding them toward the approach that aligns with their interests and objectives.
Whether settling or litigating, the overarching goal remains to secure fair compensation for the victim, addressing both economic and non-economic losses resulting from the dog bite.
By carefully weighing the available options and considering the case’s specific circumstances, individuals can make informed decisions to pursue the most effective path toward resolution.
Monetary Compensation for Dog Bite Injuries
Dog bite victims seeking monetary compensation have several avenues to address their losses, encompassing various damages.
Medical expenses represent a fundamental component, covering the costs associated with initial treatment, surgery, rehabilitation, and any ongoing medical care that the dog bite necessitates. This includes expenses for all hospital visits, medications, and therapy sessions aimed at physical or psychological recovery.

Lost earnings or income constitute another significant category of compensation. If the dog bite results where the victim is not working, temporarily or permanently, the damages sought may encompass the income or income lost during the recovery period. This extends to factors such as reduced earning capacity or the loss of future earnings due to the long-term consequences of the injury.
Pain and suffering damages address the non-economic impact of a dog bite on the victim’s life. This category considers the physical pain endured, the emotional distress experienced, and the overall reduction in the victim’s quality of life.
Courts assess the extent of these intangible losses, often relying on the evidence presented during legal proceedings to quantify appropriate compensation.
Compensation for disfigurement or scarring resulting from the dog bite is another aspect of a claim or lawsuit. Visible scars or permanent disfigurement can significantly affect an individual’s self-esteem and daily life.
Courts recognize the long-term consequences of such injuries and may award damages to address the emotional and psychological toll associated with disfigurement.
Victims may, in some cases, recover damages for loss of consortium. This type of compensation acknowledges the effects of the dog bite on the victim’s relationships and companionships, particularly in cases where the injuries result in a diminished ability to provide emotional support or participate in familial or spousal activities.
By comprehensively addressing economic losses, non-economic effects, disfigurement, and loss of consortium, dog bite victims can seek a holistic compensation package that accounts for the full spectrum of consequences resulting from the incident.
Building a robust case and presenting compelling evidence enhances the likelihood of securing fair and just monetary compensation for the various hardships resulting from a dog bite.
Speak With an Experienced Dog Bite Lawyer in Your Area Today

Ted R. Lorenz, Dog Bite Lawyer
If you recently sustained injuries in a dog attack or bite incident, you must consult with a personal injury attorney in your area as quickly as possible. Your attorney can explore your legal options and file a claim with the dog owner’s insurance company. They may also represent you during all settlement negotiations or litigate your case to a resolution in court.
